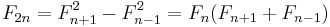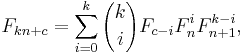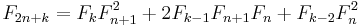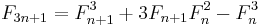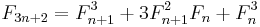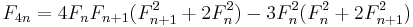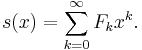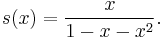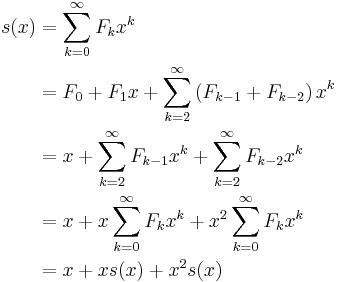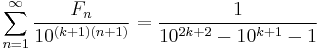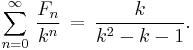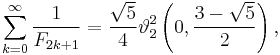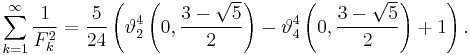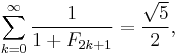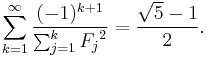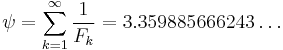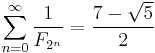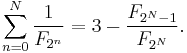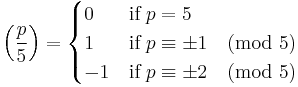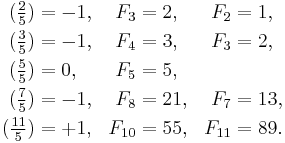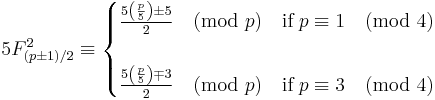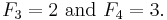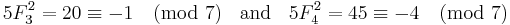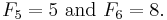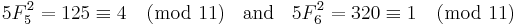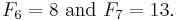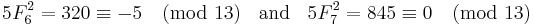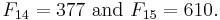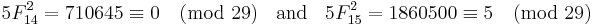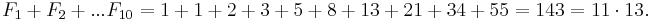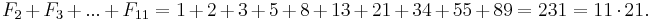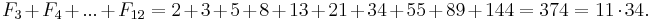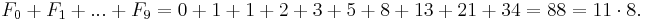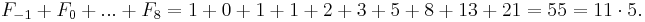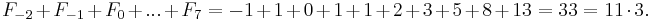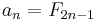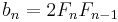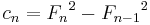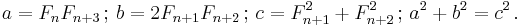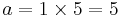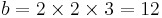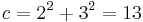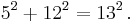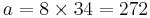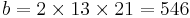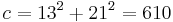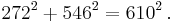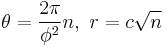Fibonacci number
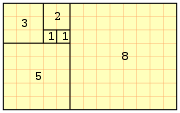

In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following sequence:
By definition, the first two Fibonacci numbers are 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two. Some sources omit the initial 0, instead beginning the sequence with two 1s.
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
with seed values
The Fibonacci sequence is named after Leonardo of Pisa, who was known as Fibonacci (a contraction of filius Bonacci, "son of Bonaccio"). Fibonacci's 1202 book Liber Abaci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics, although the sequence had been previously described in Indian mathematics.[2][3]
Fibonacci numbers are used in the analysis of financial markets, in strategies such as Fibonacci retracement, and are used in computer algorithms such as the Fibonacci search technique and the Fibonacci heap data structure. The simple recursion of Fibonacci numbers has also inspired a family of recursive graphs called Fibonacci cubes for interconnecting parallel and distributed systems. They also appear in biological settings,[4] such as branching in trees, arrangement of leaves on a stem, the fruitlets of a pineapple,[5] the flowering of artichoke, an uncurling fern and the arrangement of a pine cone.[6]
Origins
The Fibonacci sequence was well known in ancient India, where it was applied to the metrical sciences (prosody), before it was known in Europe. Developments have been attributed to Pingala (200 BCE), Virahanka (6th century CE), Gopāla (c.1135 CE), and Hemachandra (c.1150 CE).[7]
The motivation came from Sanskrit prosody, where long syllables have duration 2 and short syllables have duration 1. Any pattern of duration n can be formed by adding a short syllable to a pattern of duration n − 1, or a long syllable to a pattern of duration n − 2; thus the prosodists showed that the number of patterns of duration n is the sum of the two previous numbers in the sequence. Later authors gave algorithms for ranking and unranking these patterns (e.g. finding the kth pattern of duration n), and discovered the higher-order Fibonacci numbers. Donald Knuth reviews this work in The Art of Computer Programming.[8][9]
In the West, the sequence was studied by Leonardo of Pisa, known as Fibonacci, in his Liber Abaci (1202).[10] He considers the growth of an idealised (biologically unrealistic) rabbit population, assuming that: a newly-born pair of rabbits, one male, one female, are put in a field; rabbits are able to mate at the age of one month so that at the end of its second month a female can produce another pair of rabbits; rabbits never die and a mating pair always produces one new pair (one male, one female) every month from the second month on. The puzzle that Fibonacci posed was: how many pairs will there be in one year?
- At the end of the first month, they mate, but there is still only 1 pair.
- At the end of the second month the female produces a new pair, so now there are 2 pairs of rabbits in the field.
- At the end of the third month, the original female produces a second pair, making 3 pairs in all in the field.
- At the end of the fourth month, the original female has produced yet another new pair, the female born two months ago produces her first pair also, making 5 pairs.
At the end of the nth month, the number of pairs of rabbits is equal to the number of new pairs (which is the number of pairs in month n-2) plus the number of pairs alive last month. This is the nth Fibonacci number.[11]
List of Fibonacci numbers
The first 50 Fibonacci numbers (sequence A000045 in OEIS), denoted Fn, for n = 0, 1, 2, ... ,49 are:[12][13]
-
F0= 0 F1= 1 F2= 1 F3= 2 F4= 3 F5= 5 F6= 8 F7= 13 F8= 21 F9= 34 F10= 55 F11= 89 F12= 144 F13= 233 F14= 377 F15= 610 F16= 987 F17= 1.597 F18= 2584 F19= 4.181 F20= 6.765 F21= 10.946 F22= 17.711 F23= 28.657 F24= 46.368 F25= 75.025 F26= 121.393 F27= 196.418 F28= 317.811 F29= 514.229 F30= 832.040 F31= 1.346.269 F32= 2.178.309 F33= 3.524.578 F34= 5.702.887 F35= 9.227.465 F36= 14.930.352 F37= 24.157.817 F38= 39.088.169 F39= 63.245.986 F40= 102.334.155 F41= 165.580.141 F42= 267.914.296 F43= 433.494.437 F44= 701.408.733 F45= 1.134.903.170 F46= 1.836.311.903 F47= 2.971.215.073 F48= 4.807.526.976 F49= 7.778.742.049
The sequence can also be extended to negative index n using the re-arranged recurrence relation
which yields the sequence of "negafibonacci" numbers satisfying
Thus the complete sequence is
Properties
Every 3rd number of the sequence is even and more generally, every kth number of the sequence is a multiple of Fk. Thus the Fibonacci sequence is an example of a divisibility sequence. In fact, the Fibonacci sequence satisfies the stronger divisibility property
The Fibonacci numbers are also an example of a complete sequence, meaning every positive integer can be written as a sum of Fibonacci numbers, using any one number at most once.
Relation to the golden ratio

Closed-form expression
Like every sequence defined by linear recurrence, the Fibonacci numbers have a closed-form solution. It has become very well known as Binet's formula, even though it was already known by Abraham de Moivre:[14]
where
is the golden ratio (sequence A001622 in OEIS).
That
follows from the defining equation above.
The Fibonacci recursion
is similar to the defining equation of the golden ratio in the form
which is also known as the generating polynomial of the recursion.
| Proof by induction |
|---|
|
Any root of the equation above satisfies By definition and Both Linear combinations of series
All thus-defined series satisfy the Fibonacci recursion Requiring that and establishing the base cases of the induction, proving that
Therefore, for any two starting values, a combination |
Computation by rounding
Since 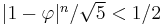 for all
for all  , the number
, the number 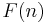 is the closest integer to
is the closest integer to 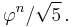 Therefore it can be found by rounding, or in terms of the floor function:
Therefore it can be found by rounding, or in terms of the floor function:
Similarly, if you already know that the number F is a Fibonacci number, you can determine its index within the sequence by
Limit of consecutive quotients
Johannes Kepler observed that the ratio of consecutive Fibonacci numbers converges. He wrote that "as 5 is to 8 so is 8 to 13, practically, and as 8 is to 13, so is 13 to 21 almost”, and concluded that the limit approaches the golden ratio 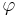 .[15]
.[15]
This convergence does not depend on the starting values chosen, excluding 0, 0. For example, the initial values 19 and 31 generate the sequence 19, 31, 50, 81, 131, 212, 343, 555 ... etc. The ratio of consecutive terms in this sequence shows the same convergence towards the golden ratio.
| Proof |
|---|
|
In brief, Fibonacci numbers are approximately exponential: More formally, it must always follow from the explicit formula that for any real because |
Decomposition of powers of the golden ratio
Since the golden ratio satisfies the equation
this expression can be used to decompose higher powers 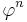 as a linear function of lower powers, which in turn can be decomposed all the way down to a linear combination of
as a linear function of lower powers, which in turn can be decomposed all the way down to a linear combination of 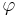 and 1. The resulting recurrence relationships yield Fibonacci numbers as the linear coefficients:
and 1. The resulting recurrence relationships yield Fibonacci numbers as the linear coefficients:
This expression is also true for 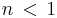 if the Fibonacci sequence
if the Fibonacci sequence 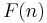 is extended to negative integers using the Fibonacci rule
is extended to negative integers using the Fibonacci rule 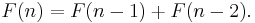
Matrix form
A 2-dimensional system of linear difference equations that describes the Fibonacci sequence is
or
The eigenvalues of the matrix A are  and
and 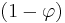 , and the elements of the eigenvectors of A,
, and the elements of the eigenvectors of A, 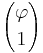 and
and 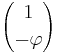 , are in the ratios
, are in the ratios  and
and 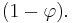 Using these facts, and the properties of eigenvalues, we can derive a direct formula for the nth element in the fibonacci series:
Using these facts, and the properties of eigenvalues, we can derive a direct formula for the nth element in the fibonacci series:
This matrix has a determinant of −1, and thus it is a 2×2 unimodular matrix. This property can be understood in terms of the continued fraction representation for the golden ratio:
The Fibonacci numbers occur as the ratio of successive convergents of the continued fraction for  , and the matrix formed from successive convergents of any continued fraction has a determinant of +1 or −1.
, and the matrix formed from successive convergents of any continued fraction has a determinant of +1 or −1.
The matrix representation gives the following closed expression for the Fibonacci numbers:
Taking the determinant of both sides of this equation yields Cassini's identity
Additionally, since 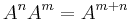 for any square matrix
for any square matrix  , the following identities can be derived:
, the following identities can be derived:
In particular, with 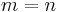 ,
,
For another way to derive the 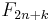 formulas see the "EWD note" by Dijkstra.[16]
formulas see the "EWD note" by Dijkstra.[16]
Recognizing Fibonacci numbers
The question may arise whether a positive integer  is a Fibonacci number. Since
is a Fibonacci number. Since 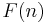 is the closest integer to
is the closest integer to 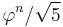 , the most straightforward, brute-force test is the identity
, the most straightforward, brute-force test is the identity
which is true if and only if  is a Fibonacci number. In this formula,
is a Fibonacci number. In this formula, 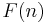 can be computed rapidly using any of the previously discussed closed-form expressions.
can be computed rapidly using any of the previously discussed closed-form expressions.
Alternatively, a positive integer  is a Fibonacci number if and only if one of
is a Fibonacci number if and only if one of 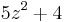 or
or 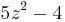 is a perfect square.[17]
is a perfect square.[17]
A slightly more sophisticated test uses the fact that the convergents of the continued fraction representation of 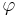 are ratios of successive Fibonacci numbers. That is the inequality
are ratios of successive Fibonacci numbers. That is the inequality
(with coprime positive integers  ,
, 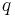 ) is true if and only if
) is true if and only if  and
and 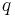 are successive Fibonacci numbers. From this one derives the criterion that
are successive Fibonacci numbers. From this one derives the criterion that  is a Fibonacci number if and only if the closed interval
is a Fibonacci number if and only if the closed interval
contains a positive integer.[18] For 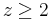 , it is easy to show that this interval contains at most one integer, and in the event that
, it is easy to show that this interval contains at most one integer, and in the event that  is a Fibonacci number, the contained integer is equal to the next successive Fibonacci number after
is a Fibonacci number, the contained integer is equal to the next successive Fibonacci number after  . Somewhat remarkably, this result still holds for the case
. Somewhat remarkably, this result still holds for the case 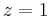 , but it must be stated carefully since
, but it must be stated carefully since 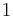 appears twice in the Fibonacci sequence, and thus has two distinct successors.
appears twice in the Fibonacci sequence, and thus has two distinct successors.
Identities

Most identities involving Fibonacci numbers draw from combinatorial arguments. F(n) can be interpreted as the number of sequences of 1s and 2s that sum to n − 1, with the convention that F(0) = 0, meaning no sum will add up to −1, and that F(1) = 1, meaning the empty sum will "add up" to 0. Here the order of the summands matters. For example, 1 + 2 and 2 + 1 are considered two different sums and are counted twice. This is discussed in further detail at Young–Fibonacci lattice.
First identity
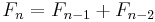
- For n > 1.
- The nth Fibonacci number is the sum of the previous two Fibonacci numbers.
| Proof |
|---|
|
We must establish that the sequence of numbers defined by the combinatorial interpretation above satisfy the same recurrence relation as the Fibonacci numbers (and so are indeed identical to the Fibonacci numbers). The set of F(n + 1) ways of making ordered sums of 1s and 2s that sum to n may be divided into two non-overlapping sets. The first set contains those sums whose first summand is 1; the remainder sums to n − 1, so there are F(n) sums in the first set. The second set contains those sums whose first summand is 2; the remainder sums to n − 2, so there are F(n − 1) sums in the second set. The first summand can only be 1 or 2, so these two sets exhaust the original set. Thus F(n + 1) = F(n) + F(n−1). |
Second identity
- The sum of the first n Fibonacci numbers is the (n + 2)nd Fibonacci number minus 1.
| Proof |
|---|
|
We count the number of ways summing 1s and 2s to n + 1 such that at least one of the summands is 2. As before, there are F(n + 2) ways summing 1s and 2s to n + 1 when n ≥ 0. Since there is only one sum of n + 1 that does not use any 2, namely 1 + ... + 1 (n + 1 terms), we subtract 1 from F(n + 2). Equivalently, we can consider the first occurrence of 2 as a summand. If, in a sum, the first summand is 2, then there are F(n) ways to the complete the counting for n − 1. If the second summand is 2 but the first is 1, then there are F(n − 1) ways to complete the counting for n − 2. Proceed in this fashion. Eventually we consider the (n + 1)th summand. If it is 2 but all of the previous n summands are 1s, then there are F(0) ways to complete the counting for 0. If a sum contains 2 as a summand, the first occurrence of such summand must take place in between the first and (n + 1)th position. Thus F(n) + F(n − 1) + ... + F(0) gives the desired counting. By induction:
|
Third identity
This identity has slightly different forms for Fj, depending on whether j is odd or even.
The sum of the first n − 1 Fibonacci numbers, Fj, such that j is odd, is the (2n)th Fibonacci number.
The sum of the first n Fibonacci numbers, Fj, such that j is even, is the (2n + 1)th Fibonacci number minus 1.
| Proofs |
|---|
|
1: j is odd By induction for F2n: A basis case for this could be F1 = F2. 2: j is even By induction for F2n+1: A basis case for this could be F0 = F1 − 1. |
| Alternative proof |
|---|
|
By using identity 1 we can construct a telescoping sum: If the summands are the Fibonacci numbers with even index, the proof is very similar. Summing both cases yields identity 2. |
Fourth identity
| Proof |
|---|
|
This identity can be established in two stages. First, we count the number of ways summing 1s and 2s to −1, 0, ..., or n + 1 such that at least one of the summands is 2. By our second identity, there are F(n + 2) − 1 ways summing to n + 1; F(n + 1) − 1 ways summing to n; ...; and, eventually, F(2) − 1 way summing to 1. As F(1) − 1 = F(0) = 0, we can add up all n + 1 sums and apply the second identity again to obtain
On the other hand, we observe from the second identity that there are
......
Adding up all n + 1 sums, we see that there are
Since the two methods of counting refer to the same number, we have
Finally, we complete the proof by subtracting the above identity from n + 1 times the second identity. |
Fifth identity
- The sum of the squares of the first n Fibonacci numbers is the product of the nth and (n + 1)th Fibonacci numbers.
| Proof |
|---|
|
Although this identity can be established by either induction or direct, albeit messy, algebraic manipulation, perhaps the most elegant and most insightful method is by a simple geometric argument. Consider the Fibonacci Rectangles constructed in previous sections. Using a common trick, we will compute the area of this rectangle in two different ways. But since this must yield the same answer in both cases, we know these resulting expressions must be equal, which will yield the desired identity. On the one hand, the nth rectangle is composed of n squares, whose side lengths are F(1), F(2), ... , F(n). Its area is therefore the sum of each of these squares, which is given by
On the other hand, we know that the nth rectangle has side lengths F(n) and F(n+1). Thus, its area is simply given by
Setting these expressions equal to each other completes the proof. |
Identity for doubling n
Another identity
Another identity useful for calculating Fn for large values of n is
from which other identities for specific values of k, n, and c can be derived below, including
for all integers n and k. Dijkstra[16] points out that doubling identities of this type can be used to calculate Fn using O(log n) long multiplication operations of size n bits. The number of bits of precision needed to perform each multiplication doubles at each step, so the performance is limited by the final multiplication; if the fast Schönhage-Strassen multiplication algorithm is used, this is O(n log n log log n) bit operations. Notice that, with the definition of Fibonacci numbers with negative n given in the introduction, this formula reduces to the double n formula when k = 0.
Other identities
Other identities include relationships to the Lucas numbers, which have the same recursive properties but start with L0 = 2 and L1 = 1. These properties include F2n = FnLn.
There are also scaling identities, which take you from Fn and Fn+1 to a variety of things of the form Fan+b; for instance
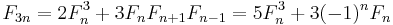 by Cassini's identity.
by Cassini's identity.
These can be found experimentally using lattice reduction, and are useful in setting up the special number field sieve to factorize a Fibonacci number. Such relations exist in a very general sense for numbers defined by recurrence relations. See the section on multiplication formulae under Perrin numbers for details.
Power series
The generating function of the Fibonacci sequence is the power series
This series has a simple and interesting closed-form solution for 
This solution can be proven by using the Fibonacci recurrence to expand each coefficient in the infinite sum defining  :
:
Solving the equation 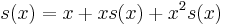 for
for 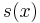 results in the closed form solution.
results in the closed form solution.
In particular, math puzzle-books note the curious value 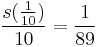 ,[20] or more generally
,[20] or more generally
for all integers  .
.
Conversely,
Reciprocal sums
Infinite sums over reciprocal Fibonacci numbers can sometimes be evaluated in terms of theta functions. For example, we can write the sum of every odd-indexed reciprocal Fibonacci number as
and the sum of squared reciprocal Fibonacci numbers as
If we add 1 to each Fibonacci number in the first sum, there is also the closed form
and there is a nice nested sum of squared Fibonacci numbers giving the reciprocal of the golden ratio,
Results such as these make it plausible that a closed formula for the plain sum of reciprocal Fibonacci numbers could be found, but none is yet known. Despite that, the reciprocal Fibonacci constant
has been proved irrational by Richard André-Jeannin.
Millin series gives a remarkable identity:[21]
which follows from the closed form for its partial sums as N tends to infinity:
Primes and divisibility
Fibonacci primes
A Fibonacci prime is a Fibonacci number that is prime (sequence A005478 in OEIS). The first few are:
- 2, 3, 5, 13, 89, 233, 1597, 28657, 514229, ...
Fibonacci primes with thousands of digits have been found, but it is not known whether there are infinitely many.[22]
Fkn is divisible by Fn, so, apart from F4 = 3, any Fibonacci prime must have a prime index. As there are arbitrarily long runs of composite numbers, there are therefore also arbitrarily long runs of composite Fibonacci numbers.
With the exceptions of 1, 8 and 144 (F1 = F2, F6 and F12) every Fibonacci number has a prime factor that is not a factor of any smaller Fibonacci number (Carmichael's theorem).[23]
144 is the only nontrivial square Fibonacci number.[24] Attila Pethő proved[25] in 2001 that there are only finitely many perfect power Fibonacci numbers. In 2006, Y. Bugeaud, M. Mignotte, and S. Siksek proved that only 8 and 144 are non-trivial perfect powers.[26]
No Fibonacci number greater than F6 = 8 is one greater or one less than a prime number.[27]
Any three consecutive Fibonacci numbers, taken two at a time, are relatively prime: that is,
- gcd(Fn, Fn+1) = gcd(Fn, Fn+2) = 1.
More generally,
Prime divisors of Fibonacci numbers
The divisibility of Fibonacci numbers by a prime p is related to the Legendre symbol 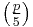 which is evaluated as follows:
which is evaluated as follows:
If p is a prime number then 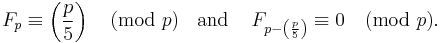 [30][31]
[30][31]
For example,
It is not known whether there exists a prime p such that 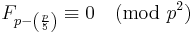 . Such primes (if there are any) would be called Wall-Sun-Sun primes.
. Such primes (if there are any) would be called Wall-Sun-Sun primes.
Also, if p ≠ 5 is an odd prime number then:[32]
Examples of all the cases:
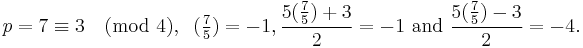
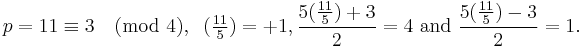
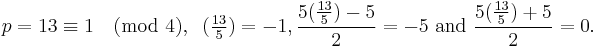
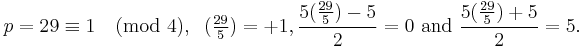
For odd n, all odd prime divisors of Fn are ≡ 1 (mod 4), implying that all odd divisors of Fn (as the products of odd prime divisors) are ≡ 1 (mod 4).[33][34]
For example, F1 = 1, F3 = 2, F5 = 5, F7 = 13, F9 = 34 = 2×17, F11 = 89, F13 = 233, F15 = 610 = 2×5×61
Divisibility by 11
The sum of any 10 consecutive Fibonacci numbers is divisible by 11; i.e.,
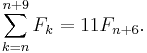
For example, let n = 1:
n = 2:
n = 3:
In fact, the identity is true for all integers n, not just positive ones:
n = 0:
n = −1:
n = −2:
Periodicity modulo n
It may be seen that if the members of the Fibonacci sequence are taken mod n, the resulting sequence must be periodic with period at most n2. The lengths of the periods for various n form the so-called Pisano periods (sequence A001175 in OEIS). Determining the Pisano periods in general is an open problem, although for any particular n it can be solved as an instance of cycle detection.
Right triangles
Starting with 5, every second Fibonacci number is the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with integer sides, or in other words, the largest number in a Pythagorean triple. The length of the longer leg of this triangle is equal to the sum of the three sides of the preceding triangle in this series of triangles, and the shorter leg is equal to the difference between the preceding bypassed Fibonacci number and the shorter leg of the preceding triangle.
The first triangle in this series has sides of length 5, 4, and 3. Skipping 8, the next triangle has sides of length 13, 12 (5 + 4 + 3), and 5 (8 − 3). Skipping 21, the next triangle has sides of length 34, 30 (13 + 12 + 5), and 16 (21 − 5). This series continues indefinitely. The triangle sides a, b, c can be calculated directly:
These formulas satisfy 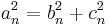 for all n, but they only represent triangle sides when
for all n, but they only represent triangle sides when 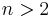 .
.
Any four consecutive Fibonacci numbers Fn, Fn+1, Fn+2 and Fn+3 can also be used to generate a Pythagorean triple in a different way:
Example 1: let the Fibonacci numbers be 1, 2, 3 and 5. Then:
Example 2: let the Fibonacci numbers be 8, 13, 21 and 34. Then:
Magnitude of Fibonacci numbers
Since 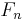 is asymptotic to
is asymptotic to 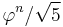 , the number of digits in
, the number of digits in 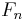 is asymptotic to
is asymptotic to 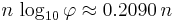 . As a consequence, for every integer
. As a consequence, for every integer 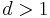 there are either 4 or 5 Fibonacci numbers with d decimal digits.
there are either 4 or 5 Fibonacci numbers with d decimal digits.
More generally, in the base  representation, the number of digits in
representation, the number of digits in 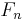 is asymptotic to
is asymptotic to 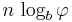 .
.
Binary strings and compositions
The Fibonacci numbers can be found in different ways in the sequence of binary strings. Due to a bijection between binary strings and compositions, every definition in terms of strings can also be given in terms of compositions, and vice versa.
- The number of strings of true length n (from the first digit to the last value 1 digit) without consecutive 0s is the Fibonacci number Fn+1. E.g., out of the 8 binary strings of true length 4, there are F5 = 5 without consecutive 0s - they are 0101, 1101, 1011, 0111 and 1111.
- The number of strings of length n without consecutive 1s is the Fibonacci number Fn+2. E.g., out of the 16 binary strings of length 4, there are F6 = 8 without consecutive 1s - they are 0000, 1000, 0100, 0010, 1010, 0001, 1001 and 0101.
(By symmetry, the number of strings of length n without consecutive 0s is also Fn+2.)
This corresponds to the following statement about compositions, quoted from OEIS A000045:
F(n)=number of compositions of n-1 with no part greater than 2.
Example: F(4)=3 because we have 3 = 1+1+1=1+2=2+1.
00 corresponds to 1+1+1, 01 corresponds to 1+2, 10 corresponds to 2+1. (compare)
| Illustrations |
|---|
.svg.png)
Consecutive 0s are marked by green dots. |
- The number of strings of true length n (from the first digit to the last value 1 digit) without even numbers of consecutive 0s or 1s is the Fibonacci number Fn. Quote from OEIS:
F(n) = number of binary words of length n beginning with 0 and having all runlengths odd;
e.g. F(6) counts 010101, 010111, 010001, 011101, 011111, 000101, 000111, 000001.
- The number of strings of length n without a even number of consecutive 1s is the Fibonacci number Fn+1.
This corresponds to the following statement about compositions, quoted from OEIS:
F(n) = number of compositions of n into odd parts;
e.g. F(6) counts 1+1+1+1+1+1, 1+1+1+3, 1+1+3+1, 1+3+1+1, 1+5, 3+1+1+1, 3+3, 5+1.
| Illustrations |
|---|
.svg.png)
Even numbers of consecutive 0s are marked by green dots, even numbers of consecutive 1s are marked in strong red. |
.svg.png)
Even numbers of consecutive 1s (corresponding to odd composition addends 3, 5, 7...) are marked in strong red. |
- Quote from OEIS: F(n) = number of compositions of n+1 with no part equal to 1
Applications
The Fibonacci numbers are important in the run-time analysis of Euclid's algorithm to determine the greatest common divisor of two integers: the worst case input for this algorithm is a pair of consecutive Fibonacci numbers.[35]
Yuri Matiyasevich was able to show that the Fibonacci numbers can be defined by a Diophantine equation, which led to his original solution of Hilbert's tenth problem.
The Fibonacci numbers occur in the sums of "shallow" diagonals in Pascal's triangle and Lozanić's triangle (see Binomial coefficient). They occur more obviously in Hosoya's triangle.
Every positive integer can be written in a unique way as the sum of one or more distinct Fibonacci numbers in such a way that the sum does not include any two consecutive Fibonacci numbers. This is known as Zeckendorf's theorem, and a sum of Fibonacci numbers that satisfies these conditions is called a Zeckendorf representation. The Zeckendorf representation of a number can be used to derive its Fibonacci coding.
The Fibonacci numbers and principle is also used in the financial markets. It is used in trading algorithms, applications and strategies. Some typical forms include: the Fibonacci fan, the Fibonacci arc, Fibonacci retracement and the Fibonacci time extension.
Fibonacci numbers are used by some pseudorandom number generators.
Fibonacci numbers are used in a polyphase version of the merge sort algorithm in which an unsorted list is divided into two lists whose lengths correspond to sequential Fibonacci numbers - by dividing the list so that the two parts have lengths in the approximate proportion φ. A tape-drive implementation of the polyphase merge sort was described in The Art of Computer Programming.
Fibonacci numbers arise in the analysis of the Fibonacci heap data structure.
The Fibonacci cube is an undirected graph with a Fibonacci number of nodes that has been proposed as a network topology for parallel computing.
A one-dimensional optimization method, called the Fibonacci search technique, uses Fibonacci numbers.[36]
The Fibonacci number series is used for optional lossy compression in the IFF 8SVX audio file format used on Amiga computers. The number series compands the original audio wave similar to logarithmic methods e.g. µ-law.[37][38]
In music, Fibonacci numbers are sometimes used to determine tunings, and, as in visual art, to determine the length or size of content or formal elements. It is commonly thought that the third movement of Béla Bartók's Music for Strings, Percussion, and Celesta was structured using Fibonacci numbers.
Since the conversion factor 1.609344 for miles to kilometers is close to the golden ratio (denoted φ), the decomposition of distance in miles into a sum of Fibonacci numbers becomes nearly the kilometer sum when the Fibonacci numbers are replaced by their successors. This method amounts to a radix 2 number register in golden ratio base φ being shifted. To convert from kilometers to miles, shift the register down the Fibonacci sequence instead.[39][40][41]
Fibonacci numbers in nature

Fibonacci sequences appear in biological settings,[4] in two consecutive Fibonacci numbers, such as branching in trees, arrangement of leaves on a stem, the fruitlets of a pineapple,[5] the flowering of artichoke, an uncurling fern and the arrangement of a pine cone.[6] In addition, numerous poorly substantiated claims of Fibonacci numbers or golden sections in nature are found in popular sources, e.g. relating to the breeding of rabbits, the spirals of shells, and the curve of waves.[42] The Fibonacci numbers are also found in the family tree of honeybees.[43]
Przemysław Prusinkiewicz advanced the idea that real instances can in part be understood as the expression of certain algebraic constraints on free groups, specifically as certain Lindenmayer grammars.[44]
A model for the pattern of florets in the head of a sunflower was proposed by H. Vogel in 1979.[45] This has the form
where n is the index number of the floret and c is a constant scaling factor; the florets thus lie on Fermat's spiral. The divergence angle, approximately 137.51°, is the golden angle, dividing the circle in the golden ratio. Because this ratio is irrational, no floret has a neighbor at exactly the same angle from the center, so the florets pack efficiently. Because the rational approximations to the golden ratio are of the form F(j):F(j + 1), the nearest neighbors of floret number n are those at n ± F(j) for some index j which depends on r, the distance from the center. It is often said that sunflowers and similar arrangements have 55 spirals in one direction and 89 in the other (or some other pair of adjacent Fibonacci numbers), but this is true only of one range of radii, typically the outermost and thus most conspicuous.[46]
The bee ancestry code
Fibonacci numbers also appear in the description of the reproduction of a population of idealized honeybees, according to the following rules:
- If an egg is laid by an unmated female, it hatches a male or drone bee.
- If, however, an egg was fertilized by a male, it hatches a female.
Thus, a male bee will always have one parent, and a female bee will have two.
If one traces the ancestry of any male bee (1 bee), he has 1 female parent (1 bee). This female had 2 parents, a male and a female (2 bees). The female had two parents, a male and a female, and the male had one female (3 bees). Those two females each had two parents, and the male had one (5 bees). This sequence of numbers of parents is the Fibonacci sequence.[47]
This is an idealization that does not describe actual bee ancestries. In reality, some ancestors of a particular bee will always be sisters or brothers, thus breaking the lineage of distinct parents.
Popular culture
Generalizations
The Fibonacci sequence has been generalized in many ways. These include:
- Generalizing the index to negative integers to produce the Negafibonacci numbers.
- Generalizing the index to real numbers using a modification of Binet's formula.[14]
- Starting with other integers. Lucas numbers have L1 = 1, L2 = 3, and Ln = Ln−1 + Ln−2. Primefree sequences use the Fibonacci recursion with other starting points in order to generate sequences in which all numbers are composite.
- Letting a number be a linear function (other than the sum) of the 2 preceding numbers. The Pell numbers have Pn = 2Pn – 1 + Pn – 2.
- Not adding the immediately preceding numbers. The Padovan sequence and Perrin numbers have P(n) = P(n – 2) + P(n – 3).
- Generating the next number by adding 3 numbers (tribonacci numbers), 4 numbers (tetranacci numbers), or more.
- Adding other objects than integers, for example functions or strings—one essential example is Fibonacci polynomials.
See also
- Golden ratio
- Lucas number
- Logarithmic spiral
- The Fibonacci Association
- Fibonacci Quarterly — an academic journal devoted to the study of Fibonacci numbers
- Negafibonacci numbers
- Fibonacci word
- Fibonacci heap
- Fibonacci cube
- Fibonacci polynomial
Notes
- ↑ http://www.quipus.it/english/Andean%20Calculators.pdf
- ↑ Parmanand Singh. "Acharya Hemachandra and the (so called) Fibonacci Numbers". Math. Ed. Siwan, 20(1):28–30, 1986. ISSN 0047-6269].
- ↑ Parmanand Singh,"The So-called Fibonacci numbers in ancient and medieval India." Historia Mathematica 12(3), 229–44, 1985.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 S. Douady and Y. Couder (1996). "Phyllotaxis as a Dynamical Self Organizing Process" (PDF). Journal of Theoretical Biology 178 (178): 255–274. doi:10.1006/jtbi.1996.0026. http://www.math.ntnu.no/~jarlet/Douady96.pdf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Jones, Judy; William Wilson (2006). "Science". An Incomplete Education. Ballantine Books. p. 544. ISBN 978-0-7394-7582-9.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 A. Brousseau (1969). "Fibonacci Statistics in Conifers". Fibonacci Quarterly (7): 525–532.
- ↑ Susantha Goonatilake (1998). Toward a Global Science. Indiana University Press. p. 126. ISBN 9780253333889. http://books.google.com/?id=SI5ip95BbgEC&pg=PA126&dq=Virahanka+Fibonacci.
- ↑ Donald Knuth (2006). The Art of Computer Programming: Generating All Trees—History of Combinatorial Generation; Volume 4. Addison-Wesley. p. 50. ISBN 9780321335708. http://books.google.com/?id=56LNfE2QGtYC&pg=PA50&dq=rhythms.
- ↑ Rachel W. Hall. Math for poets and drummers. Math Horizons 15 (2008) 10-11.
- ↑ Sigler, Laurence E. (trans.) (2002). Fibonacci's Liber Abaci. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-95419-8. Chapter II.12, pp. 404–405.
- ↑ Knott, Ron. "Fibonacci's Rabbits". University of Surrey Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences. http://www.maths.surrey.ac.uk/hosted-sites/R.Knott/Fibonacci/fibnat.html#Rabbits.
- ↑ By modern convention, the sequence begins with F0=0. The Liber Abaci began the sequence with F1 = 1, omitting the initial 0, and the sequence is still written this way by some.
- ↑ The website [1] has the first 300 Fn factored into primes and links to more extensive tables.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Weisstein, Eric W., "Fibonacci Number" from MathWorld.
- ↑ Kepler, Johannes (1966). A New Year Gift: On Hexagonal Snow. Oxford University Press. p. 92. ISBN 0198581203. Strena seu de Nive Sexangula (1611).
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 E. W. Dijkstra (1978). In honour of Fibonacci. Report EWD654
- ↑ Posamentier, Alfred; Lehmann, Ingmar (2007). The (Fabulous) FIBONACCI Numbers. Prometheus Books. p. 305. ISBN 978-1-59102-475-0.
- ↑ M. Möbius, Wie erkennt man eine Fibonacci Zahl?, Math. Semesterber. (1998) 45; 243–246.
- ↑ Vorobiev, Nikolaĭ Nikolaevich; Mircea Martin (2002). "Chapter 1". Fibonacci Numbers. Birkhäuser. pp. 5–6. ISBN 3-7643-6135-2.
- ↑ The Remarkable Number 1/89 at The Geometry Center.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W., "Millin Series" from MathWorld.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W., "Fibonacci Prime" from MathWorld.
- ↑ Ron Knott, "The Fibonacci numbers".
- ↑ J H E Cohn (1964). "Square Fibonacci Numbers Etc". Fibonacci Quarterly 2: pp. 109–113. http://math.la.asu.edu/~checkman/SquareFibonacci.html.
- ↑ A. Pethő, Diophantine properties of linear recursive sequences II, Acta Math. Paedagogicae Nyíregyháziensis, 17(2001), 81–96.
- ↑ Y. Bugeaud, M. Mignotte, S. Siksek: Classical and modular approaches to exponential Diophantine equations. I. Fibonacci and Lucas perfect powers. Ann. of Math. (2), 163(2006), 969–1018.
- ↑ Ross Honsberger Mathematical Gems III (AMS Dolciani Mathematical Expositions No. 9), 1985, ISBN 0-88385-318-3, p. 133.
- ↑ Paulo Ribenboim, My Numbers, My Friends, Springer-Verlag 2000.
- ↑ Su, Francis E., et al. "Fibonacci GCD's, please.", Mudd Math Fun Facts.
- ↑ Paulo Ribenboim (1996), The New Book of Prime Number Records, New York: Springer, ISBN 0-387-94457-5, p. 64.
- ↑ Franz Lemmermeyer (2000), Reciprocity Laws, New York: Springer, ISBN 3-540-66957-4, ex 2.25–2.28, pp. 73–74.
- ↑ Lemmermeyer, ex. 2.28, pp. 73–74.
- ↑ Lemmermeyer, ex. 2.27 p. 73.
- ↑ The website [2] has the first 300 Fibonacci numbers factored into primes.
- ↑ Knuth, Donald E. (1997). The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 1: Fundamental Algorithms (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-89683-4. (p. 343).
- ↑ M. Avriel and D.J. Wilde (1966). "Optimality of the Symmetric Fibonacci Search Technique". Fibonacci Quarterly (3): 265–269.
- ↑ Amiga ROM Kernel Reference Manual, Addison-Wesley 1991.
- ↑ IFF - MultimediaWiki.
- ↑ An Application of the Fibonacci Number Representation.
- ↑ A Practical Use of the Sequence.
- ↑ Zeckendorf representation.
- ↑ "Fibonacci Flim-Flam". http://www.lhup.edu/~dsimanek/pseudo/fibonacc.htm.
- ↑ "Marks for the da Vinci Code: B–". Computer Science For Fun: CS4FN. http://www.cs4fn.org/maths/bee-davinci.php.
- ↑ Prusinkiewicz, Przemyslaw; James Hanan (1989). Lindenmayer Systems, Fractals, and Plants (Lecture Notes in Biomathematics). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97092-4.
- ↑ Vogel, H (1979). "A better way to construct the sunflower head". Mathematical Biosciences 44 (44): 179–189. doi:10.1016/0025-5564(79)90080-4.
- ↑ Prusinkiewicz, Przemyslaw; Lindenmayer, Aristid (1990). The Algorithmic Beauty of Plants. Springer-Verlag. pp. 101–107. ISBN 978-0387972978. http://algorithmicbotany.org/papers/#webdocs.
- ↑ The Fibonacci Numbers and the Ancestry of Bees.
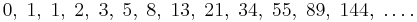
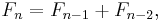
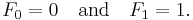
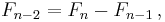
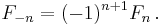
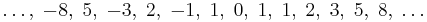
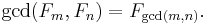
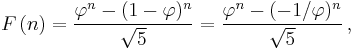
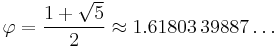

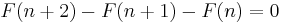
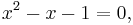
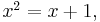 and multiplying by
and multiplying by 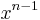 shows:
shows: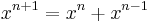
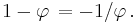 Therefore:
Therefore: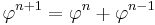
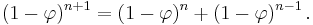
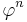 and
and  are
are 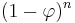 , with coefficients a and b, can be defined by
, with coefficients a and b, can be defined by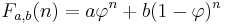 for any real
for any real 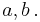
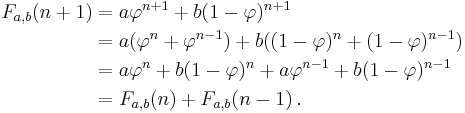
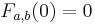 and
and 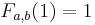 yields
yields 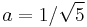 and
and 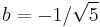 , resulting in the formula of Binet we started with. It has been shown that this formula satisfies the Fibonacci recursion. Furthermore, an explicit check can be made:
, resulting in the formula of Binet we started with. It has been shown that this formula satisfies the Fibonacci recursion. Furthermore, an explicit check can be made: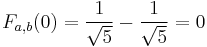
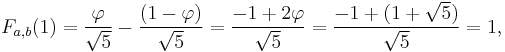
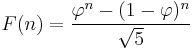 for all
for all 
 can be found such that the function
can be found such that the function  is the exact closed formula for the series.
is the exact closed formula for the series.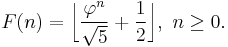
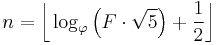
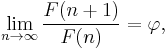
 where the constant depends on starting values – as the remaining term in the exact formula for the Fibonacci numbers becomes exponentially close to zero as n grows. Taking the ratio yields
where the constant depends on starting values – as the remaining term in the exact formula for the Fibonacci numbers becomes exponentially close to zero as n grows. Taking the ratio yields 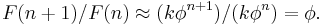
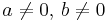
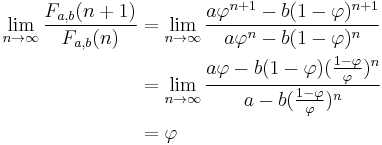
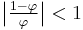 and thus
and thus 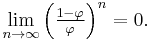
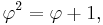
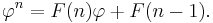
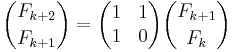
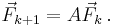
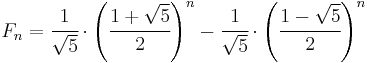
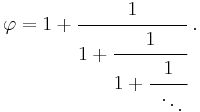
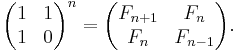
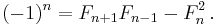
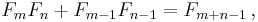
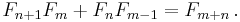
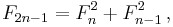
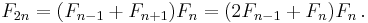
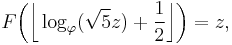
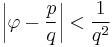
![\bigg[\varphi z-\frac{1}{z},\varphi z+\frac{1}{z}\bigg]](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/6541ea047bb5b58541e480e99740e0ce.png)
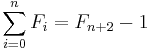
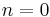 ,
, 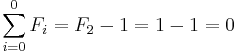 , so the equation is true for
, so the equation is true for 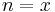 , assume
, assume 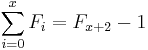 .
.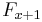 to both sides:
to both sides: 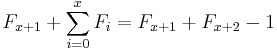 .
.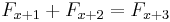 , so
, so 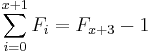 , which is the
, which is the 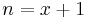 case, proving that where the equation is true for
case, proving that where the equation is true for 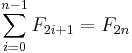
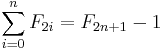
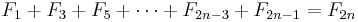
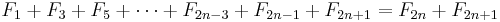
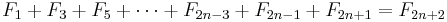
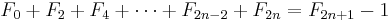
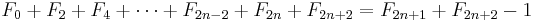
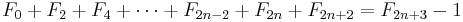
![\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} F_{2i+1} = \sum_{i=0}^{n-1} [ F_{2(i+1)}-F_{2i} ] = F_{2n}-F_{0} = F_{2n}](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/127904c0141545e8a8778f5c62fe4e7e.png)
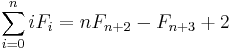
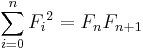
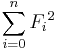 .
.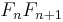 .
.